With the completions module, the user can enter information about completion tools under the Equipment > Completion Equipment menu. Here the user can define tools to be included in the tubing string, and the ratings of those tools, so that these ratings are considered in the stress calculations.
Also here, the user can define plugs to be used on the tubing string.
A note about Plug Ratings: Although plugs can be selected from within certain load cases on any string type, their ratings will only be taken into account on tubing strings.
¶ Completion Equipment
The first step to incorporating completion tools in the design is to add them to the database. This is done in the Completion Equipment tab. The lower table lists plugs, the top table lists all other types of completion items. The user can enter a name for the tool, ratings (which will be used in stress calculations), diameters (currently unused), and any notes needed to identify the tool.
An assortment of sample tools are included with StrinGnosis®. These cannot be modified, but they can be copied via right-click, and the copy can be edited as needed.
Plugs are listed separately because they have a secondary capability: they can also be used to modify the internal pressure profile in certain stress loads.
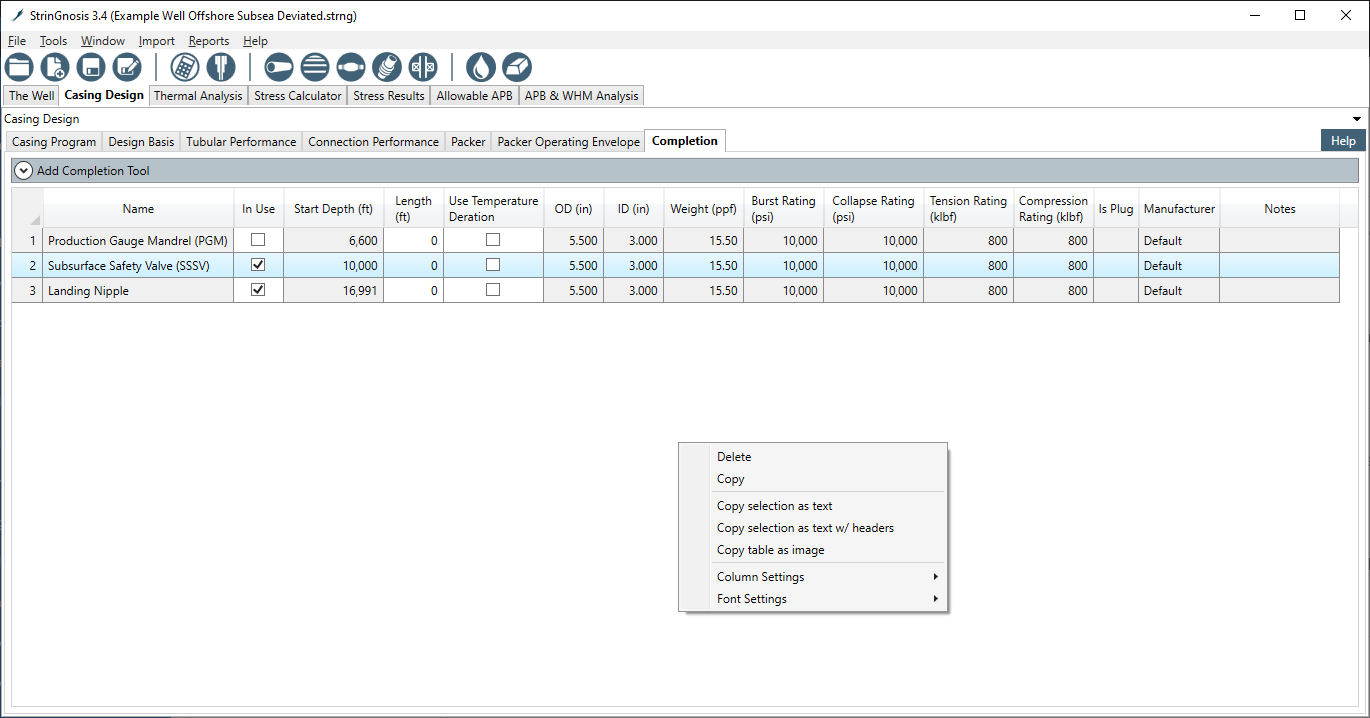
¶ In-Use Completion Equipment
Once a tool has been added to the database in the Completion Equipment tab, it is available in the In-Use Completion Equipment tables. Here, the designer can select which items are to be used in the current design and where on the tubing string they will appear.
The columns in this table are as follows:
- Name: the name of the tool as given in the Completion Equipment tables
- Plug: a display-only checkbox indicating whether the item is a plug
- In Use: with this checkbox, the designer selects which items are to be used in the current design
- Depth: the depth at which the selected item is installed on the tubing string, in MD
- Length: the length of the selected tool
- Use Temperature Deration: currently temperature deration is always used on completion tools
- ID, OD: the diameters of the tool
- Burst, Collapse, Tension, Compression Rating: the ratings that will be used by the stress calculator at the defined depths
- Manufacturer: describes the source of the tool parameters. "Default" and "User-Defined" are always available
- Notes: any text the designer added to the tool description in the Completion Equipment table
- Completion Equipment Conflicts
The completion tools chosen for a particular design are stored in the StrinGnosis® project file. When a project file is first opened, the tool descriptions are read in and compared to those in the user's database. If any tool has the same name as one in the database, but different parameters, this is marked as a conflict, and the conflicted tool is listed in the Completion Equipment Conflicts tab.
¶ Resolving Conflicts
The user has three options for handling conflicts. The conflicted tool should be inspected to determine where the conflict occurs, and the designer must choose which version of the tool to use. Then the user can:
- Prefer the database version. If the tool in the database is considered to be the correct version, the user can switch to the In-Use Completion Equipment tab and click the InUse checkbox next to that tool. That tool will be the one used at that depth and the version in the project file will be removed.
- Prefer the project file version. If the tool in the project file (the conflicted tool) is considered to be the correct version, it must be added to the database. Clicking the button in the lower left of the Conflicts tab achieves this purpose. Then the newly added tool will automatically be marked In-Use, and will be the version used at that depth in the stress calculations.
- Prefer the project file version without adding it to the database. By default, the version from the project file is the version used in the calculations. If the user takes no action, this tool will be used for all calculations on this project, but will not be added to the database (and so will not be available to use in other projects), and will still be marked as a conflict the next time the project is opened.